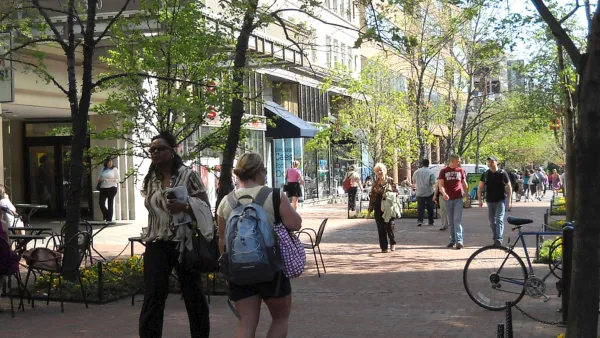New research sheds light on how the brain responds to urban environments and architecture.

The built environment, writes Jared Green for the American Society of Landscape Architects, "is directly linked with happiness and well-being, and too often urban environments fail to put people at ease." Justin Hollander, professor of urban and environmental planning and policy at Tufts University, says "we are deeply influenced by our surroundings" thanks to our "automatic (non-conscious) response to shapes, patterns, and colors."
"As we now understand, humans are drawn to landscapes that provide a refuge, a sense of safety, and prospect, a view of the entire scene, which supports that sense of safety. Storytelling is also important in landscapes, whether they are gardens, parks, or streetscapes. Humans are drawn to landscapes that provide clear sequences." In his experiments, Hollander uses eye-tracking technology to quantify the effects of various environments on the human brain. "Hollander said eye tracking software shows that New Urbanist-style communities, which have homes closer to the street; traditional architecture that mimic faces; and sidewalks all “encourage walking.” If a pedestrian can see a sequence — one, two, three, four homes in a row — they are more likely to want to walk down that row."
"According to Nikos Salingaros, professor of mathematics, architecture, urban, and complexity theory at the University of Texas at San Antonio, architects today are wed to a style rooted in 1920s Germany — the Bauhaus — that creates an unhealthy built environment" composed of "stylistically irrelevant glass boxes" that create cognitive stress in the human brain. Salingaros suggests that healthy environments are those that privilege human connectivity and the human scale–"intimate networks that are comfortable to humans." Architect and author Ann Sussman also suggests solutions for mitigating the effects of existing forms. In Somerville, Massachusetts, "the negative impact of the blank concrete wall of a parking garage was mitigated through public art and greenery."
Because "environments that are easier to fixate on cause less cognitive stress" and have a powerful impact on public health, argues Hollander, "planners, landscape architects, and architects have a responsibility to design a built environment that increases well-being."
FULL STORY: New Research: The Built Environment Impacts Our Health and Happiness More Than We Know

National Parks Layoffs Will Cause Communities to Lose Billions
Thousands of essential park workers were laid off this week, just before the busy spring break season.

Retro-silient?: America’s First “Eco-burb,” The Woodlands Turns 50
A master-planned community north of Houston offers lessons on green infrastructure and resilient design, but falls short of its founder’s lofty affordability and walkability goals.

Delivering for America Plan Will Downgrade Mail Service in at Least 49.5 Percent of Zip Codes
Republican and Democrat lawmakers criticize the plan for its disproportionate negative impact on rural communities.

Test News Post 1
This is a summary

Test News Headline 46
Test for the image on the front page.

Balancing Bombs and Butterflies: How the National Guard Protects a Rare Species
The National Guard at Fort Indiantown Gap uses GIS technology and land management strategies to balance military training with conservation efforts, ensuring the survival of the rare eastern regal fritillary butterfly.
Urban Design for Planners 1: Software Tools
This six-course series explores essential urban design concepts using open source software and equips planners with the tools they need to participate fully in the urban design process.
Planning for Universal Design
Learn the tools for implementing Universal Design in planning regulations.
EMC Planning Group, Inc.
Planetizen
Planetizen
Mpact (formerly Rail~Volution)
Great Falls Development Authority, Inc.
HUDs Office of Policy Development and Research
NYU Wagner Graduate School of Public Service