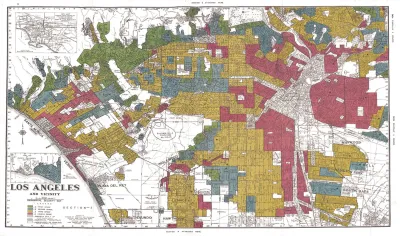
Our fair housing laws enshrine an approach that prohibits us from explicitly referring to race, even in programs intended to undo the harm caused by racism. Now restorative housing policy is attempting to directly confront this history.
The era of cellphone videos has forced white America to finally acknowledge the obvious patterns of racial inequity in policing. But in other parts of society we still cling to the idea that racial inequity is the result of “a few bad apples” rather than a core feature of the system itself.
Among the most consequential instances of this willful blindness has been our approach to fair housing. In response to centuries of unjust housing and land use policies (public and private) that target Black people and others specifically based on their race, our fair housing laws enshrine an “all lives matter” approach which actively prohibits us from explicitly referring to race even in programs intended to undo the harm caused by this history.
A new generation of local housing policymakers is attempting to directly confront this history, but fair housing law leads to convoluted policies that offer to further racial equity only indirectly through income or geographic targeting. This attempt to address racial injustice by proxy has become one of the defining failures of housing policy today. Colorblindness is fundamentally at odds with what is strategically and emotionally necessary for us to move forward as a people.
Bearing Witness to a Crime
In 1966, the apartheid regime in South Africa forcibly displaced more than 20,000 people of color from their homes in central Cape Town’s District 6. The area, a dense and racially mixed working-class community with thriving businesses and homes, had been designated a “white area” under the Group Areas Act. Under the law, only white people were allowed to own or rent property in desirably located areas like District 6. Stores and homes were bulldozed to make way for new housing for whites only. People were forcibly relocated at gunpoint (sometimes taking only suitcases) to racially segregated townships on the cape flats, miles from public services and community institutions. Previously District 6 had been home to strong mixed-race community institutions including soccer clubs, musical groups, and churches. But the apartheid system required racial sorting, so these institutions were destroyed along with the buildings of District 6. Social capital built over decades was erased in months.
For Americans, it is easy to see this shameful moment as a violent crime.
What has been harder for Americans to acknowledge is that at the same time...
FULL STORY: Restorative Housing Policy: Can We Heal the Wounds of Redlining and Urban Renewal?

Analysis: Cybertruck Fatality Rate Far Exceeds That of Ford Pinto
The Tesla Cybertruck was recalled seven times last year.

National Parks Layoffs Will Cause Communities to Lose Billions
Thousands of essential park workers were laid off this week, just before the busy spring break season.

Retro-silient?: America’s First “Eco-burb,” The Woodlands Turns 50
A master-planned community north of Houston offers lessons on green infrastructure and resilient design, but falls short of its founder’s lofty affordability and walkability goals.

Test News Post 1
This is a summary

Analysis: Cybertruck Fatality Rate Far Exceeds That of Ford Pinto
The Tesla Cybertruck was recalled seven times last year.

Test News Headline 46
Test for the image on the front page.
Urban Design for Planners 1: Software Tools
This six-course series explores essential urban design concepts using open source software and equips planners with the tools they need to participate fully in the urban design process.
Planning for Universal Design
Learn the tools for implementing Universal Design in planning regulations.
EMC Planning Group, Inc.
Planetizen
Planetizen
Mpact (formerly Rail~Volution)
Great Falls Development Authority, Inc.
HUDs Office of Policy Development and Research
NYU Wagner Graduate School of Public Service




























