City Observatory research shows that urban regions where residents drive less and rely more on other travel modes have more independent restaurants and more varied dining options. Bon appetit for walking, bicycling and public transit.

City Observatory recently used data compiled by Yelp to compute the market share of chains in the nation’s largest metro areas. Overall, about a quarter of all restaurants are part of a chain, but that fraction varies widely across metro areas. We think that a high market share of independent restaurants is likely a good indicator of a thriving and diverse food scene, and is a strong amenity for many metro areas.
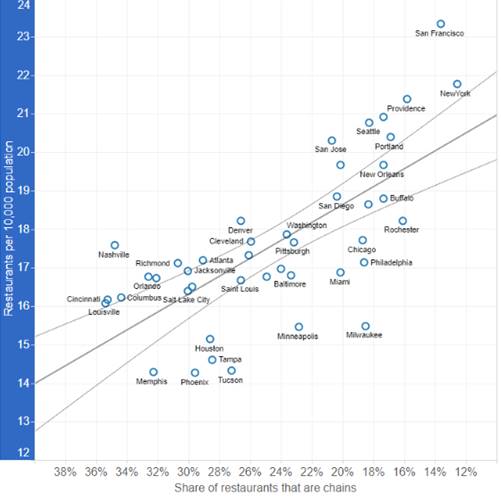
We’re not sure what the driving factors are that contribute to the more robust health of independent restaurants relative to chains in some metros, but we had a hunch. Metro areas vary widely in their level of car dependence, indicated by the average number of miles driven per person per day. In the typical large metro area, that figure is about 25 miles per person per day, but is far lower in compact, transit-served metros, and noticeably higher in sprawling, car-dependent metros.
So we took U.S. DOT estimates of the number of miles driven per person per day in large metro areas and compared it with Yelp’s data on the market share of chain restaurants in those same metros.

The data show a strong positive relationship between miles driven and chain restaurant market share. Metros where people drive more have a higher fraction of chain restaurants. For example, New York, Portland, and New Orleans all have a very low share of chain restaurants (less than 20 percent), and also have very low rates of driving per capita. Places where people drive a lot (Atlanta, Charlotte and Orlando) tend to have very high proportions of chain restaurants (more than 30 percent). Overall, each additional mile driven per day is associated with an 0.6 percentage point increase in the share of chain restaurants in a metropolitan area.
We can conjecture why this might be. If people travel more by car, then it may be more important for restaurants to be visible and accessible by car, whether located along highways or in strip malls. National brands and advertising may be relatively more important to gaining consumer awareness than they are in cities where people drive less. If people spend less time driving in cities because they are more compact, or more accessible by transit, biking and walking, that may provide more niches for smaller scale independent restaurants, compared to formula-driven chains. Often times traffic levels on streets and arterials are location factors for national chains: unless a site has so many thousands of cars passing per day, they won’t consider opening a restaurant. That kind of rationale may lead to more chain restaurants in places where people drive more.
This could also be more evidence for our Green Dividend: People who drive less spend less money on cars and gasoline, and have more money to spend on food, including supporting their local independent restaurants.
Regardless of the exact reasons, the strength of this finding is striking. It suggests that if you want to have more consumer choice and more independent entrepreneurship in your local restaurant scene, you want to have a less car-dependent transportation system. Our auto dependency may be on of the things fueling the banal sameness typically associated with chains.
FULL STORY: How Driving Ruins Local Flavor

Analysis: Cybertruck Fatality Rate Far Exceeds That of Ford Pinto
The Tesla Cybertruck was recalled seven times last year.

National Parks Layoffs Will Cause Communities to Lose Billions
Thousands of essential park workers were laid off this week, just before the busy spring break season.

Retro-silient?: America’s First “Eco-burb,” The Woodlands Turns 50
A master-planned community north of Houston offers lessons on green infrastructure and resilient design, but falls short of its founder’s lofty affordability and walkability goals.

Test News Post 1
This is a summary

Analysis: Cybertruck Fatality Rate Far Exceeds That of Ford Pinto
The Tesla Cybertruck was recalled seven times last year.

Test News Headline 46
Test for the image on the front page.
Urban Design for Planners 1: Software Tools
This six-course series explores essential urban design concepts using open source software and equips planners with the tools they need to participate fully in the urban design process.
Planning for Universal Design
Learn the tools for implementing Universal Design in planning regulations.
EMC Planning Group, Inc.
Planetizen
Planetizen
Mpact (formerly Rail~Volution)
Great Falls Development Authority, Inc.
HUDs Office of Policy Development and Research
NYU Wagner Graduate School of Public Service




























