Emissions from electricity generation are decreasing while those from transportation are increasing. If communities don't increase housing density to change travel patterns, it will only get worse, but the challenges may be insurmountable.

"While emissions from electrical plants fell in 2015, driven down partly by the rapid growth of large solar facilities, the amount of greenhouse gases spewed by cars and planes rose," reported David R. Baker for the San Francisco Chronicle in June on the California Greenhouse Gas Emission Inventory - 2017 Edition.
Illustrating why it is so difficult to reduce those transportation emissions, Liam Dillon reported for the Los Angeles Times on March 6 on the necessity to reduce driving in Southern California to meet climate goals, and the resistance by local communities to making the necessary land use changes that will change travel patterns.
“You can’t be pro-environment and anti-housing,” said Marlon Boarnet, chair of the Department of Urban Planning and Spatial Analysis at USC’s Price School of Public Policy, who has advised state climate regulators on land-use issues. “You can’t be anti-sprawl and anti-housing. This is something that has not been very well understood.”
The Southern California Association of Governments (SCAG), the metropolitan planning organization (MPO) for Los Angeles, Imperial, Orange, Riverside, San Bernardino and Ventura counties, has to prepare a regional transportation plan and sustainable communities strategy that shows how it will reduce greenhouse gas emissions resulting from transportation, as do the state's other 17 MPOs, according to SB 375, the Sustainable Communities and Climate Protection Act of 2008.
But those efforts haven’t been enough. In a series of reports over the last year, climate regulators have said California needed to reduce driving by an additional 15% over what regional governments have already planned to meet the 2030 greenhouse gas targets. That means even more closely packed housing than previously anticipated will be needed.
Hasan Ikhrata, SCAG's executive director, believes the new push to reduce driving is too difficult to achieve. “We’re going to do our best, but I think it’s too ambitious, to be honest with you,” Ikhrata said.
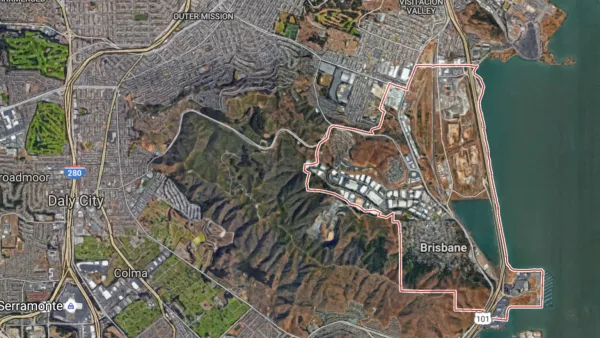
Of course, resistance to increased density is not restricted to Southern California. Reporting on July 28 from the small Bay Area city of Brisbane, population 4,700, just south of San Francisco in San Mateo County, Dillon describes the opposition to a development proposal located adjacent to a commuter rail station that could create a substantial dent in the region's housing crisis by providing 4,400 homes on 660 acres of vacant brownfield. But it's more than just local opposition to increased density that makes smart growth difficult in the Golden State.
The project, Brisbane Baylands, reveals how few incentives local governments have to accept large developments — even as the state is pushing to lower housing costs and funnel growth toward existing cities and nearby mass transit to combat climate change.
Under California’s tax system, Brisbane also earns more money if it rejects the current plan in favor of potential alternatives with more hotel rooms and space for businesses — but no homes.
While the "anti-development fervor" that has gripped Brisbane is the main focus of Dillon's piece, he also describes the challenges posed by the regulatory and economic framework that make smart growth so challenging in the state's coastal regions.
Hat tip to David McCoard.
FULL STORY: A Bay Area developer wants to build 4,400 sorely needed homes. Here's why it won't happen

Analysis: Cybertruck Fatality Rate Far Exceeds That of Ford Pinto
The Tesla Cybertruck was recalled seven times last year.

National Parks Layoffs Will Cause Communities to Lose Billions
Thousands of essential park workers were laid off this week, just before the busy spring break season.

Retro-silient?: America’s First “Eco-burb,” The Woodlands Turns 50
A master-planned community north of Houston offers lessons on green infrastructure and resilient design, but falls short of its founder’s lofty affordability and walkability goals.

Test News Post 1
This is a summary

Analysis: Cybertruck Fatality Rate Far Exceeds That of Ford Pinto
The Tesla Cybertruck was recalled seven times last year.

Test News Headline 46
Test for the image on the front page.
Urban Design for Planners 1: Software Tools
This six-course series explores essential urban design concepts using open source software and equips planners with the tools they need to participate fully in the urban design process.
Planning for Universal Design
Learn the tools for implementing Universal Design in planning regulations.
EMC Planning Group, Inc.
Planetizen
Planetizen
Mpact (formerly Rail~Volution)
Great Falls Development Authority, Inc.
HUDs Office of Policy Development and Research
NYU Wagner Graduate School of Public Service